Introduction To Blue Crab Seasonality
Blue crabs are a species of decapod crustaceans belonging to the family Portunidae. They get their name from the vibrant blue coloration that characterizes their carapace (shell).
Characteristics of Blue Crabs And Seasonal Impact
These omnivorous creatures have five pairs of legs with modified front appendages called chelipeds, which they use for catching prey as well as defense. Blue crabs exhibit sexual dimorphism, where males typically have bright blue claws while females possess red-tipped claws.
ONLINE SHIPPING

We’re excited to announce that we will soon be offering online shipping for our premium Maryland Blue Crabs! This new service will allow you to enjoy the fresh, succulent taste of our crabs from the comfort of your own home, no matter where you are. To make sure you’re among the first to experience this convenience, we invite you to visit our website and sign up for our notification email. By doing so, you’ll be promptly informed as soon as our shipping service goes live. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to have the finest Maryland Blue Crabs delivered straight to your doorstep. Click the button to visit the store to sign-up! 🦀📦🌍
Why Knowing ‘When Blue Crabs Are In Season’ Matters
Understanding the seasonality of blue crabs is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows us to make informed decisions regarding sustainable harvesting practices. By knowing when these crustaceans are most abundant in different regions, we can avoid overfishing during vulnerable periods and help maintain healthy populations for future generations.
Secondly, understanding blue crab seasonality is vital for recreational crabbers and commercial fishermen alike. It enables them to plan their fishing trips or harvests effectively and maximize their chances of success by targeting peak abundance periods when more crabs are available.
Furthermore, comprehending the seasonality patterns helps us appreciate and preserve this delicacy’s culinary value. Different stages in a blue crab’s life cycle, such as molting or mating, influence the taste and texture of their meat.
By knowing when these events occur, culinary enthusiasts can make informed choices about the best time to indulge in soft-shell crabs or select the most flavorful mature crabs for various dishes. Understanding blue crab seasonality contributes to our overall knowledge of marine ecosystems.
Scientists have asked themselves many times the same question you are searching for the answer to (when are blue crabs in season). By studying the factors that influence their life cycles and distribution patterns, scientists gain insights into broader environmental processes. Blue crabs serve as indicators of water quality and ecosystem health, making their seasonal behavior a valuable tool for monitoring changes in coastal habitats.

Determining When Blue Crabs Are In Season
Key Environmental Factors for Blue Crab Seasonality
The seasonal occurrence of blue crabs is influenced by a myriad of factors. Two crucial elements impacting their timing are environmental conditions and the intricate interplay between their reproductive cycles and molting patterns. These factors work in harmony, dictating when blue crabs emerge, reproduce, molt, and eventually enter periods of dormancy.
Impact of Temperature and Salinity on Blue Crab Seasons
Blue crabs are highly attuned to their environment and show remarkable sensitivity to changes in temperature and salinity levels. Warmer water temperatures stimulate their metabolic activity, leading to increased feeding behaviors and growth rates. For optimal survival and reproduction, blue crabs require a narrow range of temperatures typically found in coastal areas.
Salinity levels also play a key role in the seasonal dynamics of blue crabs. They prefer brackish or moderately salty waters where they can thrive.
However, extreme salinity fluctuations can disrupt their reproductive success or force them to migrate in search of more favorable conditions. Blue crab populations are known to concentrate near estuaries where freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the ocean.
The Role of Reproductive and Molting Cycles in Blue Crab Seasonality
The reproductive cycles and molting patterns intricately connected with each other dictate when blue crab seasons occur. Blue crabs reproduce through external fertilization; males transfer sperm into specialized receptacles on the female’s abdomen during mating. After fertilization occurs, females carry eggs externally attached to their abdomen until they hatch into larvae.
Molting is a critical process for crustaceans like blue crabs as it allows growth by shedding old exoskeletons that have become too constricting. Molting frequency varies depending on the age, size, and sex of individual crabs.
Younger individuals molt more frequently as they grow rapidly, while older crabs may molt less often. The molting process leaves blue crabs temporarily vulnerable, as their soft shells harden after a period of time.
These reproductive and molting processes intertwine with environmental conditions to determine when blue crab seasons occur. Environmental cues, such as temperature and salinity changes, trigger the onset of reproductive activity.
Females typically undergo a rapid molt shortly before producing eggs, ensuring their new exoskeleton is strong enough to protect the developing embryos. Consequently, these biological events align with the optimal environmental conditions for successful reproduction, ensuring the survival and future generations of blue crabs.
Understanding the seasonality of blue crabs involves comprehending both the external influences of environmental conditions and the intricate sequence of reproductive cycles and molting patterns. Temperature and salinity fluctuations strongly impact their behavior and distribution throughout different seasons.
Moreover, these factors directly influence crucial life processes like mating, egg production, larval development, and molting frequency. By unraveling this complex interplay between biology and environment, we can gain insights into when blue crabs emerge from dormancy or hibernation periods and witness their remarkable lifecycle unfold in coastal ecosystems.
Spring: The Start of Blue Crab Season
Signs of Blue Crab Activity in the Spring
As the winter frost retreats, nature comes alive with the signs of a new season. Similarly, the coastal areas where blue crabs reside witness a surge of activity during springtime. As temperatures begin to rise, the first inklings of blue crab awakening become apparent.
In these early stages, keen observers might notice an increase in blue crab sightings and interactions along the shorelines. This resurgence is a testament to their remarkable resilience and adaptability.
Migration Patterns: When Blue Crabs Begin Their Seasonal Journey
During this time of rejuvenation, blue crabs embark on remarkable migratory journeys from their overwintering grounds in deeper waters towards estuaries or other shallow coastal areas. The warming water temperatures stimulate their instinctual need to seek out more favorable environments for feeding and reproduction. They undertake these migrations not only driven by temperature but also by changes in food availability and salinity preferences.
The migration patterns of blue crabs are influenced by various factors such as ocean currents, water temperature gradients, and seasonal variations in food abundance. These movements are not solely limited to long-distance travel; rather, they can also involve shorter migrations within local estuaries as they search for optimal conditions for their activities.
Feeding and Mating: Indicators of Blue Crab Season Peak
With the arrival of spring and favorable environmental conditions, blue crabs exhibit heightened feeding and mating behaviors that mark this phase as truly transformative. As they settle into suitable habitats like estuaries or marshes with abundant food sources, such as bivalves or small fish species, their voracious appetite becomes evident.
During this period, female blue crabs mature sexually while males actively compete for their attention through complex courtship rituals. Male crabs perform intricate dance-like displays with gentle touches using specialized appendages called swimmerets to charm potential mates.
These behaviors are essential for the continuation of their species and contribute to the thriving population of blue crabs. As spring unfolds, blue crabs undergo a remarkable awakening, transitioning from a period of relative dormancy into a state of heightened activity.
Their migrations towards estuaries and coastal areas become more apparent, as does their increased appetite and vibrant mating rituals. These early signs of the blue crab season set the stage for the subsequent abundance that characterizes their peak season in summer.
Summer Season: Peak of Blue Crab Season
Blue crab Population Surge in Summer Months
During the summer season, blue crabs experience a remarkable increase in population, making it the prime time for crabbers and seafood enthusiasts alike. The warm water temperatures create ideal conditions for their growth and reproduction, leading to a surge in their numbers along coastal areas and estuaries. This is absolutely the peak of when blue crabs are in season. This abundance of blue crabs is a result of their complex life cycle, which involves various stages and behaviors.
Optimal Conditions for Blue Crab Growth in Summer
Blue crabs thrive in waters that maintain temperatures between 70 to 80 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 27 degrees Celsius). When the temperature reaches this range during the summer months, it stimulates their metabolism, promoting rapid growth and facilitating reproductive processes. The warmth of the water accelerates their molting cycles and encourages frequent feeding, ultimately contributing to the population explosion observed during this period.
Molting and Vulnerability: Key Aspects of Summer Blue Crab Season
Molting is an essential part of a blue crab’s life cycle. It is during this process that they shed their old exoskeletons to grow larger ones.
While molting allows them to increase in size, it also renders them vulnerable as they temporarily lack protection from predators. During these delicate moments, blue crabs hide in protected areas such as seagrass beds or burrows until their new exoskeletons harden.
During the summer season when water temperatures are optimal for growth, blue crabs molt more frequently compared to other times of the year. Their increased molting activity adds excitement to crabbing as soft-shell crabs become more abundant.
Soft-shell crabs are essentially blue crabs that have recently molted and have not fully hardened their new shells yet. These soft-shelled delicacies are highly sought after by seafood enthusiasts for their tender texture and delicate flavor.
Summer Delicacy: Soft-Shell Crabs in Peak Season
Soft-shell crabs are a culinary delight cherished by seafood enthusiasts around the world. These succulent crustaceans are harvested during the brief window between molting and shell hardening when their shells are pliable and edible.
With their delicate flavor and unique, slightly sweet taste, soft-shell crabs have become a sought-after delicacy in many coastal communities. To capture these delectable creatures at their softest state, skilled crabbers carefully monitor blue crab populations during the summer season.
They deploy specialized traps and nets to catch blue crabs as they molt, ensuring that only the finest soft-shell specimens make it to market. The demand for soft-shell crabs reaches its peak during this time, making it an opportune moment for both crabbers and seafood connoisseurs alike.
The summer season serves as a period of abundance for blue crabs. The optimal water temperatures during this time promote rapid growth, frequent molting, and increased reproductive activity among these creatures.
Crabbers take advantage of this population explosion to harvest prized soft-shell crabs—a delicacy enjoyed by many seafood enthusiasts. By understanding the dynamics of blue crab populations during the summer months, we can fully appreciate the significance of timing when it comes to indulging in these delectable creatures.

Fall: Blue Crabs Preparing for Off-Season
Transitioning to Colder Months: Blue Crab Behaviors
As the vibrant hues of autumn adorn the coastal landscapes, blue crabs start their preparations for the imminent arrival of winter. These astute creatures possess an innate ability to sense environmental changes, prompting them to make critical adjustments in their behavior and physiology. With a keen eye on survival, blue crabs begin their arduous journey towards sustaining themselves through the upcoming colder months.
Blue Crabs Migrating: Preparing for Winter
One of the remarkable strategies employed by blue crabs during the fall season is migration. Sensing the dropping temperatures and waning food sources in their current habitats, these resourceful crustaceans embark on a remarkable journey towards deeper waters or warmer regions.
This instinctual movement allows them to seek areas that provide more favorable conditions for survival during winter. Driven by a primal urge to find suitable sanctuaries, blue crabs undertake impressive migrations that can span vast distances.
Some individuals may migrate from estuaries and shallow coastal waters to deeper offshore areas where water temperatures remain relatively stable throughout the year. Others may choose to move along coastlines in search of warmer pockets created by ocean currents or protected bays and lagoons.
Energy Conservation Strategies for Off-Season Survival
With winter approaching, blue crabs adjust their metabolic rates and decrease their feeding activity significantly. As resources become scarce due to seasonal changes in prey availability, these astute creatures conserve energy by reducing their hunting efforts. This reduced feeding behavior is crucial for them to cope with diminishing food sources during winter when prey populations often experience declines.
During this period of decreased feeding activity, blue crabs primarily rely on stored energy reserves accumulated during previous seasons of abundance. By conserving energy through reduced feeding efforts, they ensure that enough resources are available to sustain vital physiological processes during the dormant winter months. A delicate balance between energy conservation and survival.
The transition towards winter dormancy is a delicate balancing act for blue crabs. They must allocate their limited energy stores wisely, ensuring that essential life functions continue while avoiding excessive energy expenditure. This careful allocation extends beyond feeding behavior and includes other vital activities such as reproduction, molting, and maintaining physiological equilibrium.
Blue crabs expertly navigate this intricate dance of conserving energy without jeopardizing their chances of survival once spring arrives. Their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions throughout the seasons showcases the extraordinary resilience and versatility of these captivating crustaceans.
Whether it’s embarking on lengthy migrations or reducing feeding activity, blue crabs demonstrate a remarkable understanding of their environment. With each passing fall season, they remind us of nature’s intricacies and the awe-inspiring strategies employed by creatures to ensure their continued existence in a world constantly in flux.
Winter: Dormancy Period in Blue Crab Season
During the winter season, blue crabs adopt various strategies to survive the harsh conditions and ensure their long-term survival. These strategies involve adaptations that allow them to protect themselves and conserve energy until more favorable circumstances arise.
Survival Strategies During Blue Crab Off-Season
Blue crabs have evolved several remarkable adaptations that enable them to cope with the challenges posed by winter conditions. One of the most prominent strategies is burrowing into mud or sand for protection.
By burrowing deep into the substrate, blue crabs create a safe haven where they can shield themselves from extreme temperatures, strong currents, and predators. This burrowing behavior is facilitated by their powerful claws and specialized leg structures designed for digging.
Blue crabs are remarkably efficient at creating burrows, often tunneling several feet beneath the surface. These burrows provide them with a stable environment that helps maintain a relatively constant temperature, protecting them from freezing waters above.
Burrowing for Protection in Cold Months
The process of burrowing involves the blue crab using its powerful pincers to excavate an entrance hole in the substrate. Once inside, they continue digging further until they reach a suitable depth where they can hibernate comfortably.
The entrance hole is carefully constructed in such a way that it allows water circulation while preventing excessive exposure to cold temperatures or predators. The insulation provided by surrounding mud or sand acts as a buffer against extreme temperature fluctuations.
This protective layer helps maintain a relatively stable thermal environment within their shelters during colder months when surface waters become inhospitable. The intricate network of tunnels created by blue crabs also serves as a refuge for other aquatic organisms seeking shelter from adverse winter conditions.
Metabolic Adjustments During the Blue Crab Winter Season
In addition to burrowing, blue crabs slow down their metabolism significantly during the winter season as a means of conserving energy. This metabolic slowdown allows them to survive with minimal food consumption, as their physiological processes are significantly reduced. By lowering their metabolic rate, they can conserve limited energy reserves and endure extended periods of dormancy.
This adaptation is crucial because food availability decreases dramatically in colder waters, making it challenging for blue crabs to sustain their regular feeding activities. By conserving energy through a reduced metabolic rate, they can survive without relying heavily on external food sources until more favorable conditions return.
During the winter season, blue crabs employ a range of survival strategies to endure harsh conditions. Their ability to burrow into mud or sand provides them with protection from freezing water temperatures and predators.
Furthermore, by slowing down their metabolism and conserving energy, these resilient creatures can sustain themselves even when food availability is scarce. These adaptations exemplify the remarkable resilience and resourcefulness of blue crabs in adapting to changing environmental conditions.
Regional Differences in Blue Crab Seasonality
Variations in ‘When Are Blue Crabs in Season’ Across Regions
Blue crabs, being highly adaptable creatures, exhibit variations in their seasonal patterns depending on the geographical location. The East Coast, Gulf Coast, West Coast, and other regions experience unique fluctuations in blue crab populations.
Factors such as water temperature, salinity levels, and food availability play a crucial role in determining these differences. For instance, the colder waters of the East Coast result in shorter blue crab seasons compared to the more temperate Gulf and West Coasts.
Seasonal Insights: East Coast vs. Gulf Coast vs. West Coast
On the East Coast of the United States, including states such as Maryland and Virginia, blue crabs are typically most abundant during summer months from May through September. The Chesapeake Bay region is particularly famous for its rich blue crab harvest during this time.
Moving down to the Gulf Coast states like Louisiana and Texas reveals slightly longer seasons due to milder winters and warmer waters. The peak season here stretches from April through October.
On the West Coast of North America along California’s coastlines, blue crab seasonality differs significantly due to cooler waters influenced by upwelling currents. While there isn’t a specific season for harvesting blue crabs here as on the East and Gulf Coasts, they can be found year-round with higher abundance during summer months when water temperatures are more favorable.
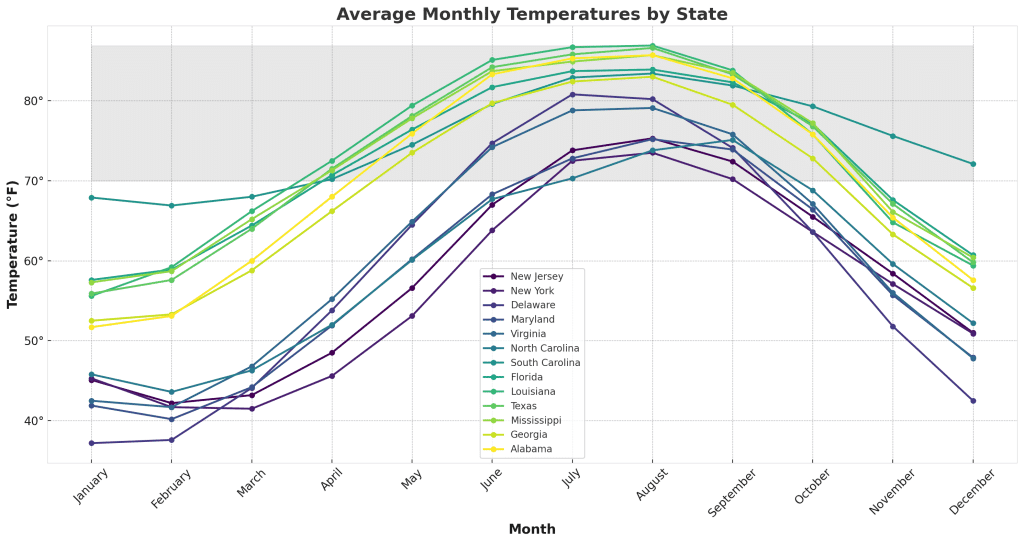
2024 Blue Crab Seasons by State
Here’s an overview of blue crab seasons in various states for 2023, highlighting the question, “When is blue crab season?” in each locale:
- Maryland: The heart of blue crab culture, Maryland’s season typically starts on April 1 and runs through December 15. This period is when the Chesapeake Bay, famous for its blue crabs, becomes a hub of crabbing activity. (Maryland Blue Crab Season 2024 begins on April 1st)
- Virginia: Neighboring Maryland, Virginia shares part of the Chesapeake Bay and begins its crab season a bit earlier, on March 17, which lasts until November 30. The state’s regulations are closely aligned with sustainable harvesting practices.
- Louisiana: Known for its unique culinary scene, Louisiana offers a year-round crabbing season, with specific periods designated for harvesting to protect crab populations during their breeding times.
- North Carolina: With a season that generally runs all year, with a peak from June to October, North Carolina’s blue crab harvest aligns with the warmer waters of its coastal regions.
- Texas, Alabama, Mississippi: These Gulf states have year-round seasons but maintain strict size and bag limits to ensure sustainability.
- Florida: Florida’s blue crab season varies by region, often year-round with peak seasons in the summer. The state’s diverse coastline offers different crabbing experiences.
- South Carolina and Georgia: Both states have year-round availability but regulate the size and quantity of crabs to promote sustainable practices.
For the most accurate and up-to-date information, I recommend visiting the provided links or directly contacting the respective state’s fisheries department.
Three Tips to Know When Crabs are in Season
Understanding when blue crabs are in season is not only about knowing the official dates but also about recognizing the natural and regulatory signs. Here are three essential tips to help you identify the best times for crabbing:
Tip 1: Stay Informed About State Regulations
State regulations are a critical factor in determining the blue crab season. These regulations are often based on preserving the crab population and ensuring sustainable harvesting.
- Regularly Check State Websites: As regulations can change, regularly visit the state fisheries websites linked earlier for the most current information.
- Subscribe to Newsletters or Alerts: Many state departments offer newsletters or alerts that provide updates on fishing seasons and regulations.
- Engage with Local Fishery Offices: Local fishery offices are a valuable resource for up-to-date information and can often provide insights beyond what’s available online.
Tip 2: Look for Seasonal Indicators in Nature
Nature itself provides cues that can indicate when the blue crab season is at its peak.
- Monitor Water Temperatures: Blue crabs are more active in warmer waters, typically when temperatures are above 70°F. Websites like NOAA’s National Ocean Service can help you track water temperatures.
- Observe Crab Behavior: Pay attention to crab behavior. Increased molting and mating activities are often signs that the season is in full swing.
- Note Environmental Changes: Changes in local flora and fauna, such as the blooming of certain plants or the arrival of migratory birds, can also coincide with the crabbing season.
Tip 3: Connect with Local Crabbing Communities
Local crabbing communities are treasure troves of information and often know the best times for crabbing based on years of experience.
- Join Local Forums and Social Media Groups: These platforms are great for getting real-time updates and tips from experienced crabbers.
- Attend Local Fishing Clubs or Meetings: Such gatherings are excellent for networking and learning from seasoned crabbers.
- Visit Local Fishing Piers and Marinas: Engaging with locals at these sites can provide valuable, firsthand information about the current state of the crabbing season.
By following these tips, you’ll be better equipped to understand and take advantage of the blue crab season in your area, ensuring a fruitful and responsible crabbing experience.
Influence of Local Climate on Blue Crab
The local climate has a profound impact on blue crab habitat and overall population dynamics within each region. Cooler climates lead to shorter growing seasons and limited breeding opportunities for blue crabs.
Conversely, warmer climates facilitate longer periods of growth and reproduction for these crustaceans. Additionally, variations in rainfall patterns can affect salinity levels within estuaries where blue crabs inhabit—altering the timing of their seasonal movements and migrations
Conclusion: Maximizing Your Blue Crab Season Experience
Understanding the regional variations in blue crab seasons is essential for both seafood enthusiasts and the fishing industry. From the East Coast to the Gulf Coast and even the West Coast, each region offers a unique opportunity to experience and indulge in these delectable crustaceans.
While temperature, salinity, and local climate influence their seasonality, it is heartening to know that blue crabs continue to adapt and thrive in diverse environments. So whether you’re savoring a Maryland crab feast or exploring the flavors of Cajun cuisine in Louisiana, blue crab seasons offer a delightful experience that can be enjoyed with enthusiasm across different parts of North America.

